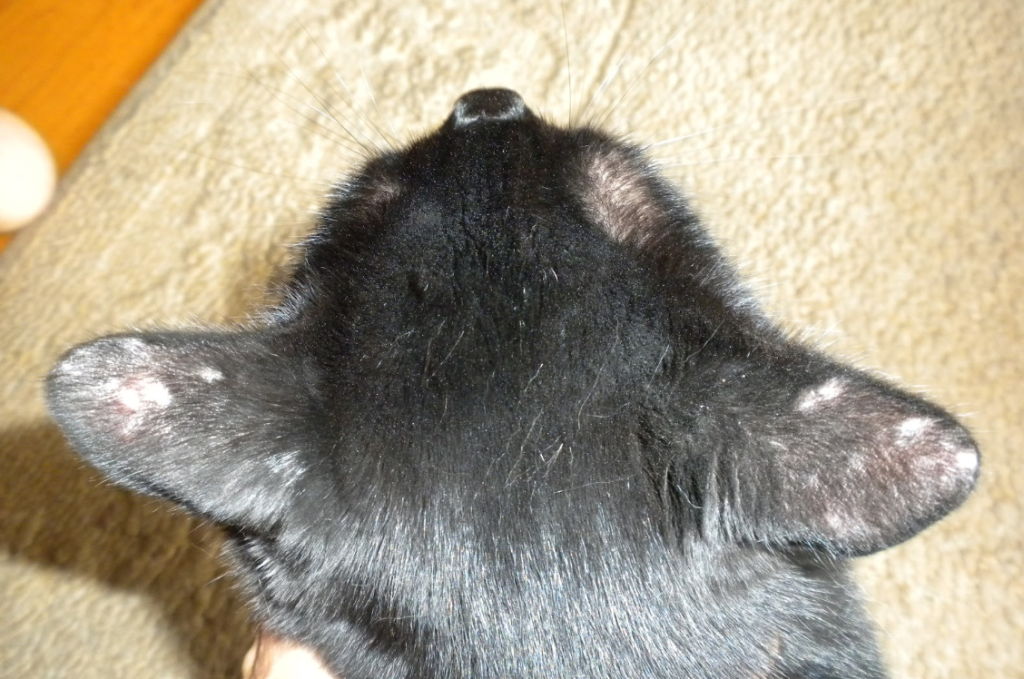
Has your furry friend been scratching their ears more than normal? Upon closer inspection, you may notice cat losing hair on ears or bald spots. Loss of hair on a cat’s ears can indicate an underlying issue. Learning the common causes and solutions can help get to the root of the problem and restore your cat’s lush coat.
Common Causes of Hair Loss on Cat’s Ears
There are several reasons a cat may start to lose hair around their ears. Here are the most common causes:
Ear Mites
Ear mites are a common parasite that feed on ear wax and oils. They cause inflammation, itching, debris buildup, head shaking, and hair loss around the ears. Ear mites affect about 10% of cats. The mites are contagious and can spread between cats through close contact.
Signs of ear mites include:
- Hair loss around the ears in patches or bald spots
- Black debris that looks like coffee grounds in the ears
- Head shaking and scratching at ears
- Redness and swelling inside the ears
Allergies
Just like humans, cats can develop environmental or food allergies. Allergic reactions cause inflammation and itchiness. Constant scratching and rubbing leads to hair loss and skin damage.
Common allergy triggers include:
- Flea bites
- Food ingredients (e.g. beef, dairy, wheat, corn)
- Environmental allergens (e.g. pollen, dust mites)
Signs of allergies include:
- Hair loss around the ears and head
- Red, moist patches on the skin
- Frequent head shaking and scratching
- Excessive licking of paws or base of tail
Bacterial or Yeast Infection
Bacteria and yeast naturally live on a cat’s skin. But an overgrowth can cause an infection. Moist, warm areas like ears are prone to infection.
Signs of an ear infection include:
- Hair loss around the ears
- Redness and swelling
- Black or yellow discharge
- Bad odor
- Head tilt or shakiness
- Loss of balance
- Increased scratching
Hormonal Imbalance
Hormonal issues may arise from thyroid disease or diabetes. The hormonal imbalance can disrupt hair growth cycles. This leads to symmetrical hair loss on both ears and sometimes the tail too.
Signs of hormonal issues include:
- Symmetrical hair loss on tips and edges of ears
- Weight gain or loss
- Increased appetite
- Lethargy
Sunburn
Cats with light-colored ears and thin hair coats are prone to sunburn. Ultraviolet radiation damages the skin and hair follicles. The ears and nose are common areas affected.
Signs of sunburn include:
- Red, flaky skin on ears and nose
- Hair loss around ear tips and edges
- Scabs or blisters
- Swelling
Autoimmune Disease
Rare autoimmune disorders can cause progressive hair loss. With alopecia, the immune system attacks the hair follicles. It often starts with small bald patches that expand over time.
Signs of alopecia include:
- Circular bald spots that worsen over time
- Hair loss without itching, redness, or sores
Stress or Trauma
Severe stress or trauma has been linked to hair loss in some cases. The excessive grooming behavior damages the skin and coat.
Stress triggers include:
- New home, pet, baby, etc.
- Loud noises like fireworks or construction
- Neglect or abuse
- Other pets bullying
Signs of stress-related hair loss:
- Over grooming of areas until bald spots form
- Aggressive hair pulling
- No other signs of skin problems
Diagnosing the Cause of Hair Loss
Since many conditions can cause ear hair loss, it’s important to have your vet examine your cat. They will review symptoms and medical history and conduct tests. This helps pinpoint the underlying problem.
Diagnostic tests may include:
- Ear exam – Looks for debris, inflammation, discharge
- Skin scraping – Checks for ear mites under a microscope
- Fungal culture – Confirms yeast overgrowth
- Blood work – Checks for hormonal or immune disorders
Your vet may also recommend:
- Biopsy – Examines skin cells to check for abnormalities
- Allergy testing – Identifies environmental and food allergies
Once the cause is found, proper treatment can begin.
7 Tips to Stop Cat Ear Hair Loss
The treatment options will vary depending on the cause. But here are some general tips to help restore hair growth and comfort:
1. Treat Ear Mites
If ear mites are the culprit, your vet will recommend ear mite medication containing ingredients like selamectin, sarolaner, or ivermectin. Treat any other cats in contact as well.
Thoroughly clean the ears to remove debris. Follow up with treatments to ensure the mites are fully eliminated.
2. Address Allergies
For environmental allergies, keep your home clean and limit exposure to triggers. An air purifier with a HEPA filter can help remove dander and pollen.
Food allergies may require an elimination diet under a vet’s guidance to identify problem ingredients. Your cat may need a hypoallergenic prescription diet.
Allergy medications like antihistamines and omega-3 fatty acids can help control symptoms. Regular bathing with an oatmeal shampoo can also soothe skin.
3. Treat Infections
Bacterial and yeast infections require medications like antibiotic, antifungal, and steroid ear drops or oral medication. Follow your vet’s directions for cleaning the ears and applying medications.
You may need to treat for up to 6 weeks and have follow up appointments to ensure the infection is gone. Keeping ears clean and dry can help prevent recurrence.
4. Address Hormonal Issues
Treatment for hormonal disorders like hypothyroidism or diabetes will include medications to regulate hormone levels. Blood tests will monitor progress. Controlling the condition should allow hair to regrow.
5. Protect from the Sun
Limit sun exposure during peak hours. Apply pet-safe sunscreen to vulnerable areas 30 minutes before going outside.
Also provide shade and fresh water when outdoors. Keep indoor cats away from windowsills receiving direct sunlight.
6. Reduce Stress
To minimize stress-related over grooming, stick to regular schedules and routines. Avoid loud noises and introductions to new pets or people. Increase playtime, cat trees, and enrichment toys to boost activity and comfort.
Medications and pheromone sprays can also curb anxiety. Consider working with a vet on behavioral modification techniques.
7. Supplements for Hair Regrowth
Certain supplements support skin and coat health:
- Omega-3 fatty acids – Found in fish oil. Helps reduce inflammation.
- Biotin – Helps produce keratin for hair growth.
- Zinc – Supports skin health and wound healing.
- Vitamin E – Has antioxidant properties that may aid hair regrowth.
Consult your vet before giving supplements to ensure safety and proper dosing for your cat.
When to See the Vet
Make an appointment right away if your cat is losing hair around their ears and:
- Has discharge, odor, head shaking, or scratching
- Has additional patches of hair loss on body
- Seems lethargic and unwell
- Hair loss spreads rapidly
Sudden or severe hair loss warrants urgent vet care to determine the cause and treatment. Seek immediate help if your cat is scratching to the point of wounding themselves.
While waiting for your appointment, avoid cleaning the cat’s ears – this could worsen some conditions. Prevent scratching by using an Elizabethan collar and keep the area clean.
Can Ear Hair Loss Grow Back?
With prompt treatment of the underlying issue, your cat has an excellent chance of regrowing hair on their ears fully.
However, in rare cases of chronic skin disease or permanent damage from severe mite infestation, the hair loss may be permanent. Still, the condition can be managed with medication and lifestyle changes to keep your cat comfortable.
Be patient during treatment, as restoring hair health takes time. Limit scratching and inflammation, while supporting skin and coat recovery. With a holistic approach, most cats with ear hair loss can regain their lush locks.
FAQs About Cat Ear Hair Loss:
What does it mean if my cat is losing hair on ears?
Hair loss around a cat’s ears signals some type of skin problem, rather than a normal shedding process. It’s often a sign of ear mites, infection, allergies, or hormonal issues. Veterinary assessment is needed to diagnose the specific cause.
How can I stop my cat scratching his ears?
To stop a cat excessively scratching their ears:
- Keep nails trimmed short
- Distract with toys when scratching starts
- Apply an Elizabethan collar to prevent scratching
- Identify and treat the underlying condition
- Use calming supplements
When should I take my cat to vet for ear hair loss?
Make a veterinary appointment right away if your cat has:
- Sudden patches of hair loss around ears
- Scratching, head shaking, or discharge
- Hair loss spreading to other parts of body
- Lethargy, appetite changes, or other signs of illness
Seek prompt vet care for diagnosis and treatment, as many causes of ear hair loss worsen without care.
Final Words
Noticing your cat losing hair on ears can be concerning. But in most cases, identifying and treating the underlying cause will allow the hair to regrow.
Get familiar with the common causes like ear mites, allergies, and infections. See your vet as soon as possible for an accurate diagnosis. Follow treatment plans, protect their ears, and be patient. With a proactive approach, your kitty’s lush ear fur should return, letting you both get back to purring and playing.


